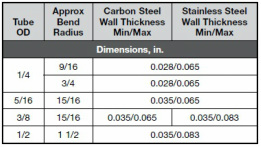
1. Type of tubing ( Fractional tubing ) -- Inch
High-quality, soft-annealed, seamless carbon steel hydraulic tubing ASTM A179 or equivalent. Hardness 72 HRB (130 HV) or less.
Fully annealed, high-quality (Type 304, 316 etc.) (seamless or welded and drawn) stainless steel hydraulic tubing ASTM A269 or A213, or equivalent.Hardness 90 HRB (200 HV or less)
High-quality, soft-annealed, seamless carbon steel hydraulic tubing ASTM A179 or equivalent. Hardness 72 HRB (130 HV) or less.
Fully annealed, high-quality (Type 304, 316 etc.) (seamless or welded and drawn) stainless steel hydraulic tubing ASTM A269 or A213, or equivalent.Hardness 90 HRB (200 HV or less)
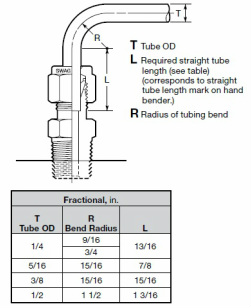
2. Tubing installation
When installing fittings near tube bends, there must be a sufficient length of straight tubing to allow the tube to be bottomed in the Swagelok tube fitting:
When installing fittings near tube bends, there must be a sufficient length of straight tubing to allow the tube to be bottomed in the Swagelok tube fitting:
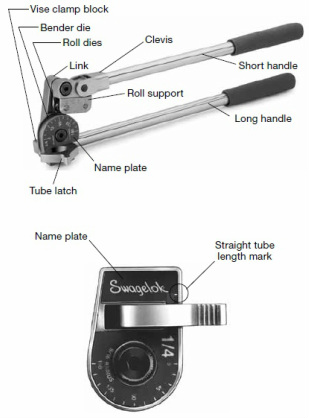
3. Tubing Bender
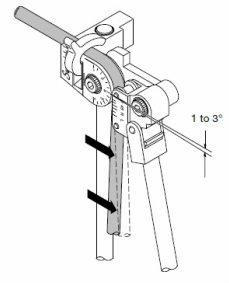
4. Springback
All tubing will exhibit springback after a bend has been completed. The amount of springback depends on the bend angle, bend radius, tubing material, and wall thickness.
Experience will help you predict the amount ofspringback. Expect to allow 1 to 3° of compensation
All tubing will exhibit springback after a bend has been completed. The amount of springback depends on the bend angle, bend radius, tubing material, and wall thickness.
Experience will help you predict the amount ofspringback. Expect to allow 1 to 3° of compensation
5. How to bend
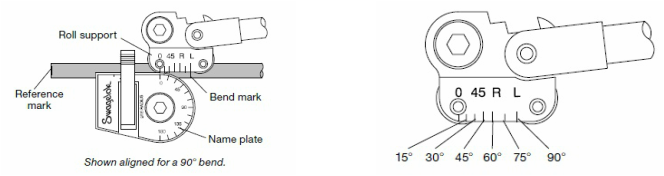
a. Normal bend
a. Normal bend
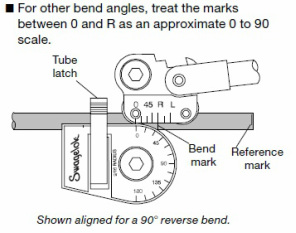
b. Reverse bend
Reference mark is the place where you are beginning the measurement
Bend mark is indicating vertex of the bend
Bend mark is indicating vertex of the bend
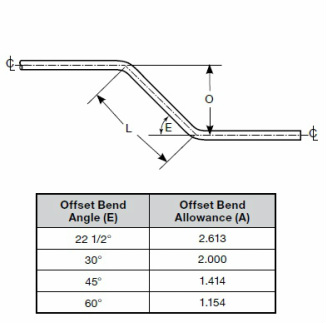
c. Offset bend
The purpose of an offset bend is to change the center line of the run, typically to avoid an obstruction. To determine the length of offset, select the offset angle (E). Then, multiply the offset dimension (O) by theoffset bend allowance (A).
L = O x A
The purpose of an offset bend is to change the center line of the run, typically to avoid an obstruction. To determine the length of offset, select the offset angle (E). Then, multiply the offset dimension (O) by theoffset bend allowance (A).
L = O x A
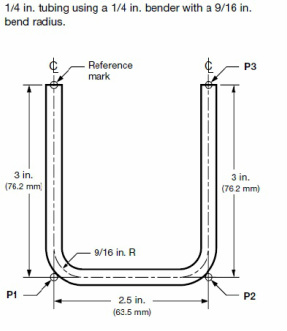
6. Example
P1 = 3 in
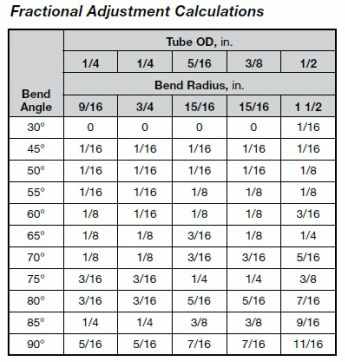
P2 = P1+2.5 in - 5/16 (see table bellow,tubing OD 1/4 bender radius 9/16 and degree of bend 90 ) = 5 3/16 in
P3 = P2 + 3 in - 5/16 (see table bellow,tubing OD 1/4 bender radius 9/16 and degree of bend 90 ) = 7 7/8 in
So total tubing needed is 7 7/8 in
P2 = P1+2.5 in - 5/16 (see table bellow,tubing OD 1/4 bender radius 9/16 and degree of bend 90 ) = 5 3/16 in
P3 = P2 + 3 in - 5/16 (see table bellow,tubing OD 1/4 bender radius 9/16 and degree of bend 90 ) = 7 7/8 in
So total tubing needed is 7 7/8 in
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed